Recent Posts
Archives
Categories
ApnaCircle
Join ApnaCircle, the professional social network chosen by Shaik Mukram and more than 35 million professionals
The Most Precious Gem of Humans
Cardiomyopathy involves a weakening of the heart muscles or structural changes in these muscles. This often leads to inadequate heart pumping or problems with the functioning of the heart. The poor heart pumping mechanism leads to accumulation of fluid in the lungs, liver, and other body systems. Cardiomyopathy is classified into three morphologic types: dilated, restrictive, and hypertrophic. When the exact cause is not known the term used is idiopathic.
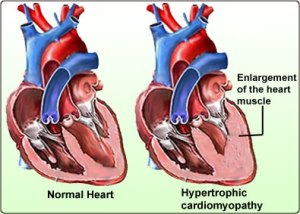
![]() Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: In this condition the heart muscles get thicker making it harder for blood to leave.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: In this condition the heart muscles get thicker making it harder for blood to leave.
![]() Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Weakening and enlargement of the heart muscles prevent it from pumping blood efficiently.
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Weakening and enlargement of the heart muscles prevent it from pumping blood efficiently.
![]() Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: This condition is associated with increased stiffness of the heart.
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: This condition is associated with increased stiffness of the heart.
 Symptoms include palpitation. difficulty with breathing (dyspnoea) and sometimes even Sudden death can occur, Complications like pulmonary oedema, arrhythmias and ascites can occur.
Symptoms include palpitation. difficulty with breathing (dyspnoea) and sometimes even Sudden death can occur, Complications like pulmonary oedema, arrhythmias and ascites can occur.
Sudden cardiac death is the most dreaded of the complications. International guidelines recommend that a risk stratification score can predict the outcome. These are the six risk factors to look for in a patient with Cardiomyopathy:
![]() Previous cardiac arrest or sustained ventricular tachycardia,
Previous cardiac arrest or sustained ventricular tachycardia,
![]() Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia,
Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia,
![]() Extreme left ventricular hypertrophy,
Extreme left ventricular hypertrophy,
![]() Unexplained syncope,
Unexplained syncope,
![]() Abnormal blood pressure response,
Abnormal blood pressure response,
![]() Family history of sudden death
Family history of sudden death
Hypertension affects about a billion individuals worldwide. It is a silent killer. If undetected and untreated it silently damages the blood vessels, heart, brain, and kidneys. A person is said to have hypertension (i.e. high blood pressure) when his arterial blood pressure is elevated above the normal range expected in his age group. There are two terms that one needs to know: Systolic BP and Diastolic BP. When a doctor records your blood pressure as 120/80 mm Hg, it means that 120 mm Hg is the systolic blood pressure (BP) and 80 mm Hg is the diastolic BP.
Based on these two blood pressure values, you may belong to one of the following groups:
Arterial hypertension is the leading cause of death in the world and the most common cause for an outpatient visit to a physician. The higher your blood pressure, the greater is the chance of heart attack, heart failure, stroke, and kidney disease. Understanding the benefits of lowering blood pressure is thus important.
A common fallacy that most people have is that a healthy lifestyle is all that is required to control hypertension. Prescription medication is the cornerstone of an effective antihypertensive therapy. Lifestyle modification can only be an adjunct, but never an alternative. It is not possible to bring down blood pressure to optimum levels by lifestyle changes alone.
Clinical trials prove that antihypertensive therapy can bring significant reduction in the incidence of stroke (by up to 40%), myocardial infarction (by up to 25%) and heart failure (by 50%). Any regimen should include lifestyle modification.
The earlier guidelines recommended a trial of lifestyle modification alone for an unspecified time before a prescription of antihypertensive medication. But recent trials do not agree to this. A greater urgency is required in attaining rapid pharmacologic control of high blood pressure so as to lessen cardiovascular risk. This is because non pharmacologic reductions in blood pressure are often small and there is a high chance of recidivism.
| BP CLASSIFICATION | SYSTOLIC BP (mm Hg) | DIASTOLIC BP (mm Hg) |
| Normal | <120 | And <80 |
| Pre Hypertensiive | 120-139 | Or 80-89 |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 140-159 | Or 90-99 |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | Or |
Aortic valve governs the orifice from the lower left chamber of the heart to the aorta. With increased degree of narrowing there is an increased impediment of blood flow leading to catastrophe. An intact aortic valve is a must so as to ensure a smooth flow of blood pumped by the left ventricular chamber into the major vessel called aorta.
The causes of aortic stenosis
![]() Bicuspid and Other Congenitally Abnormal Aortic Valves
Bicuspid and Other Congenitally Abnormal Aortic Valves
A Normal aortic valve has three thin leaflets called cusps (tricuspid). About 1% of the population is born with a bicuspid aortic valve, i.e. with only two cusps in the valve. There exists a male preponderance. Although this abnormality does not usually cause symptoms at birth these valves tend to deteriorate with age. By the time these individuals reach their 40s, 50s, and 60s aortic stenosis may develop.
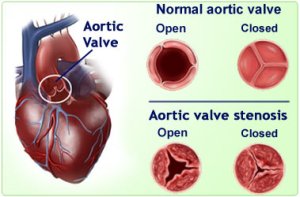 Congenital aortic stenosis from a unicuspid, bicuspid, or even abnormal tricuspid valve may cause symptoms during childhood and necessitates rectification by adolescence.
Congenital aortic stenosis from a unicuspid, bicuspid, or even abnormal tricuspid valve may cause symptoms during childhood and necessitates rectification by adolescence.
![]() Tricuspid Aortic Valve Stenosis
Tricuspid Aortic Valve Stenosis
A previously normal tricuspid aortic valve can also develop thickening and calcification. Stenosis and calcifications were formerly considered to be degenerative processes.
Currents concepts are that this type of aortic stenosis arises from an active inflammatory process.
![]() Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Scarring of the aortic valve due to rheumatic fever as a child or young adult is a rare cause in developed countries. Unfortunately rheumatic heart disease is still rampant in the developing nations.
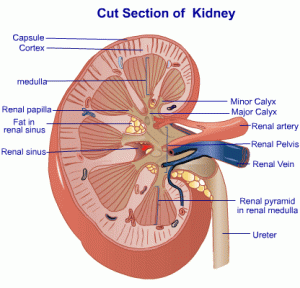
Chronic renal failure is a gradual and progressive loss of the ability of the kidneys to function normally. The change is irreversible and is due to loss of nephrons of the kidney. The nephrons are basic functioning unit of the kidney and there are normally about one million nephrons in each kidney.
The kidney is no longer able to clean toxins & waste product from blood and concentrate the urine . When patients begin to experience symptoms of kidney failure, most of their kidney function is lost. Simply it can be interpreted as kidneys gradually stopping to working.
Acute Renal Failure (ARF) is the sudden loss of kidney function. It occurs when the kidneys stop working over a period of hours, days, or in some cases, weeks.
The bean shaped organs, called kidneys need to be ‘full of beans’ to carry out the crucial task of filtering body waste and maintaining electrolyte levels in the blood. Malfunction of the kidneys could lead to accumulation of waste products, fluids, and electrolytes in the body, which could gravely endanger life.
Acute Renal Failure is also referred clinically as, a sharp increase of the serum creatinine level from baseline (i.e., an increase of at least 0.5 mg/dl) and the urine output is less than 400 ml per day (oliguria), though not strictly applicable for ARF.
Acute Renal Failure is the cause of complication in 5% of all hospital admissions. With the exclusion of relevant medical conditions, the mortality rate for ARF stands at 10%. The prognosis may be bleak if ARF is accompanied with complicated medical conditions or surgical conditions.
 Acute Renal Failure (ARF) and Chronic Kidney Disease – Are They Different?
Acute Renal Failure (ARF) and Chronic Kidney Disease – Are They Different?
The answer is ‘yes’. Acute Renal Failure is often the consequence of any untoward experience the body is subjected to; for instance – blood loss due to surgery, or medicine overdose or any injury to the body.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is often the consequence of long term illness like high blood pressure or diabetes which gradually takes a toll on the kidneys, causing them to malfunction.
The brain is the most amazing and complex organ in this universe and its research continues to throw up new facts that surprise’s us. The brain is capable of being modified or improved even as we age. It is never used to its full capacity.
1. The human brain has about 100,000,000,000 or100 billion neurons. From the age of 35 years about 7000 neurons are lost daily.
2. During early pregnancy the neurons in the fetus canmultiply at a rate 250,000 neurons/minute.
3. Brain is composed of75 to 80% water. Dehydration can affect proper functioning of brain.
4. Brain consists of60% White matter and 40% Grey matter. White is the supporting matter and Grey is the thinking matter of the brain. If the brain was a computer the grey matter would be the computer itself and the white matter its cables.
5. Adult brain weighs about3 pounds or 1300 to 1400 Grams. This is about 2% of the body weight if you weigh 150 pounds or 70 kgs. Sperm whale’s brain weighs 7800 gms.
6. Although the brain only accounts for 2 percent of our body weight but it consumes20% of the oxygenthat we breathe androughly 20 percent of our daily calories.
7.15-20% of all blood pumpedout of the heart goes directly to the brain.
8. All the thinking in the brain is aboutelectricity and chemicals. The brain is more active and thinks more at night than during the day.
9. The brain itself isincapable of feeling pain. Once the skull is opened it is possible to operate on the brain with the patient awake.
10.You can’t feel your own tickle either. The brain is smart enough to neutralize the sensation. The cerebellum sends a signal to rest of the brain of your intentions and as a result the sensation is ignored.